Data protection
Better rules for small businesses
Stricter data protection rules since May 2018 mean that citizens gain more control over their data and businesses benefit from a level playing field. One set of rules for all companies operating in the EU, wherever located. Learn what this means for your SME.
What is personal data?
Do you store use data?
You have to follow the rules.Do you process data for other companies? Then this applies to you as well.Why change the rules?
It's about trust…
Distrust of the old data protection has hampered the digital economy and it is quite possible that your business.

People think they have the information they enter online completely under control.
And help companies grow…
One set of rules for all data processing companies in the EU
Business is now easier and fairer
The new system keeps costs low and helps businesses grow
130 million euros
the cost to a business in the EU of informing 28 different data protection authorities in the old system
2.3 billion euros
the estimated economic benefits of uniform legislation
The new rules should boost the confidence of consumers and therefore businesses.
What your company needs to do
Protect the rights of the people who provide you with your data
Communication
Communicate easily.
When you request information from them, tell them who you are.
Indicate why you process the data, how long you will keep it and who will retrieve it.
Warning
If people are at serious risk of data breaches, let them know.
Access and portability
Let people access your data and share it with other companies.
Agreement
Get a clear consent to the processing of data from them.
Do you collect data from children from social networks? Check the age limit when you need parental consent.
Protection of sensitive data
Apply premium protection to information about health, race, sexual orientation, and religious and political beliefs.
Deleting data
Give people the "right to be forgotten". If they request it, delete their personal data [ndash], but only if this does not interfere with freedom of expression or scrutiny.
Marketing
Give people the right not to engage in direct marketing that uses their data.
Data transfer outside the EU
If you transfer data to countries not verified by the EU institutions, take appropriate legal action.
Profiling
If you use profiling when processing applications leading to the conclusion of a legally binding contract, eg in the case of loans, you must:
- inform your customers about it;
- in the event that a request is rejected, ensure that the entire procedure is controlled by a person, not a device;
- give the applicant the right to challenge the decision.
Protect data conceptually
Integrate data protection measures into your products and services from the earliest stages of development.
Are you processing data for another company?
Make sure you have an unassailable contract that lists each party's obligations.
Verify that you do not need a dedicated employee to protect your data
It is not always a duty. It depends on the type and amount of data you collect, whether it is your main business and whether you process it on a large scale.
Keep records
SMEs only need to keep records if they are processing data
Records should include:
- Name and contact details of the company
- Reason for data processing
- Description of the categories of data subject and personal data
- Categories of organizations that will receive the data
- Transfer of data to another country or organization
- Deadline for deletion of data, if possible
- A description of the security measures applied during processing, if possible
Anticipate impact assessments
In the case of HIGH RISK processing, it may be necessary to use an impact assessment.
Nové technologie
Automatic, systematic processing and evaluation of personal data
High-capacity monitoring of public space (eg camera system)
High-capacity processing of sensitive data, such as biometricsy
Costs in case of non-compliance with the rules
Compliance with the rules is monitored by local data protection authorities; their action is coordinated at EU level. Failure to comply with the rules can lead to high costs for the person concerned.
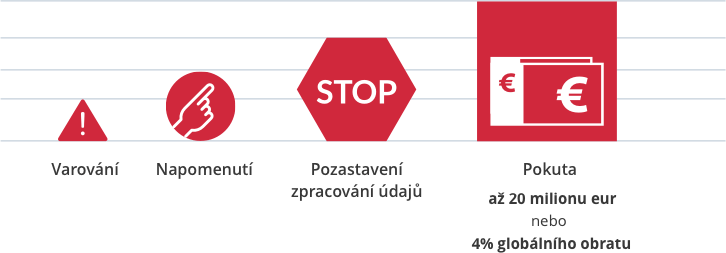
Protect your data, protect your business
This document cannot be considered as an official opinion of the European Commission and does not replace legislation.


